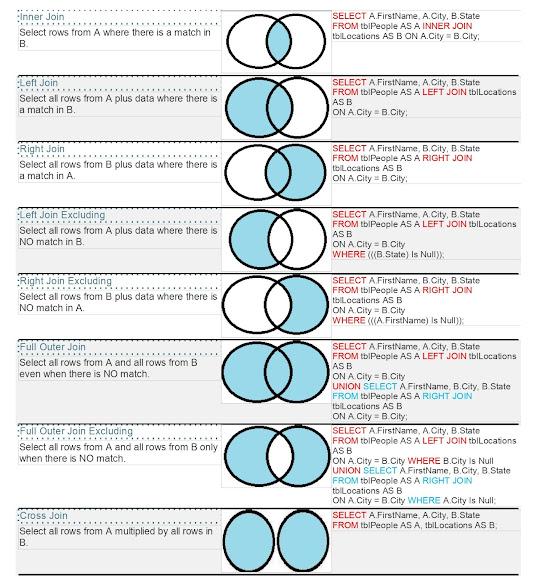
1. What are the different types of joins in MySQL? Explain with examples.
Answer:
The most common types of joins in MySQL are:
- INNER
JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables.
- LEFT
JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN): Returns all records from the left table and
the matched records from the right table. If no match, NULL is returned
for columns from the right table.
- RIGHT
JOIN (or RIGHT OUTER JOIN): Similar to LEFT JOIN but returns all
records from the right table.
- FULL
JOIN: MySQL doesn’t support FULL JOIN directly, but you can simulate
it using UNION.
Example:
-- INNER JOIN Example
SELECT orders.order_id, customers.name
FROM orders
INNER JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id =
customers.customer_id;
-- LEFT JOIN Example
SELECT orders.order_id, customers.name
FROM orders
LEFT JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id;
2. How do you find duplicate records in a table?
Answer:
To find duplicate records, use GROUP BY along with HAVING to filter groups that
occur more than once.
Code:
SELECT name, email, COUNT(*) as duplicate count
FROM users
GROUP BY name, email
HAVING duplicate count > 1;
Explanation:
This query checks for duplicate combinations of name and email in the users
table.
3. What is the difference between WHERE and HAVING
clauses?
Answer:
- WHERE:
Filters rows before grouping and aggregate functions are applied.
- HAVING:
Filters groups after grouping and aggregate functions are applied.
Example:
-- WHERE clause example (filtering rows before aggregation)
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE amount > 100;
-- HAVING clause example (filtering after aggregation)
SELECT customer_id, COUNT(*) as order_count
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id
HAVING order_count > 5;
4. What is the purpose of LIMIT in MySQL?
Answer:
LIMIT is used to specify the number of rows returned by a query. It's often
used with ORDER BY to retrieve a subset of the result set.
Code:
SELECT * FROM products
ORDER BY price DESC
LIMIT 5;
Explanation:
This query returns the top 5 most expensive products from the products table.
5. Explain how indexing works in MySQL.
Answer:
Indexes are used to speed up the retrieval of rows by creating a data structure
that allows faster searching. Indexes are particularly useful for columns used
in WHERE, JOIN, or ORDER BY clauses.
Code to create an index:
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON users (name);
Explanation:
This creates an index on the name column of the users table, speeding up
searches involving this column.
6. What is normalization? Explain the different normal
forms.
Answer:
Normalization is the process of organizing the data in the database to reduce
redundancy and dependency by dividing large tables into smaller, related
tables.
- 1st
Normal Form (1NF): Each column contains atomic values (no multiple
values in one column).
- 2nd
Normal Form (2NF): The table is in 1NF, and all non-key columns are
fully dependent on the primary key.
- 3rd
Normal Form (3NF): The table is in 2NF, and there are no transitive
dependencies (i.e., non-key columns depend on other non-key columns).
7. How do you calculate the total number of rows in a table?
Answer:
You can use the COUNT() function to calculate the number of rows in a table.
Code:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total_rows FROM users;
Explanation:
This returns the total number of rows in the users table.
8. How do you perform a self-join in MySQL?
Answer:
A self-join is when a table is joined with itself. You give the table different
aliases to treat them as separate tables.
Code:
SELECT a.name AS Employee, b.name AS Manager
FROM employees a
JOIN employees b ON a.manager_id = b.employee_id;
Explanation:
This query finds employees and their managers. The employees table is joined
with itself using aliases a and b.
9. What is a subquery in MySQL? Give an example.
Answer:
A subquery is a query nested inside another query. It can be used in SELECT, INSERT,
UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
Code:
SELECT name, email
FROM users
WHERE user_id IN (SELECT user_id FROM orders WHERE amount >
500);
Explanation:
This query retrieves users who have made orders with amounts greater than 500.
The subquery selects user_ids from the orders table.
10. How do you ensure data integrity in MySQL?
Answer:
Data integrity in MySQL is maintained using:
- Primary
Keys: Ensures uniqueness and not null for each record.
- Foreign
Keys: Ensures the integrity of relationships between tables.
- Constraints:
Enforces rules like NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK, etc.
Code to add a foreign key:
ALTER TABLE orders
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_customer
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(customer_id);
Explanation:
This adds a foreign key constraint that ensures each customer_id in the orders
table must exist in the customers table.












No comments:
Post a Comment